Understand AI Agents
An AI Agent is a powerful component in GlobalAI that acts as a specialized assistant you can build and add to your automations. Think of an agent as more than just a general chatbot. It is an AI model that you equip with a specific purpose, a defined set of knowledge, and a custom list of tools it can use.
You can use agents directly inside a workflow to make complex decisions, summarize data, or transform information as part of a larger process.
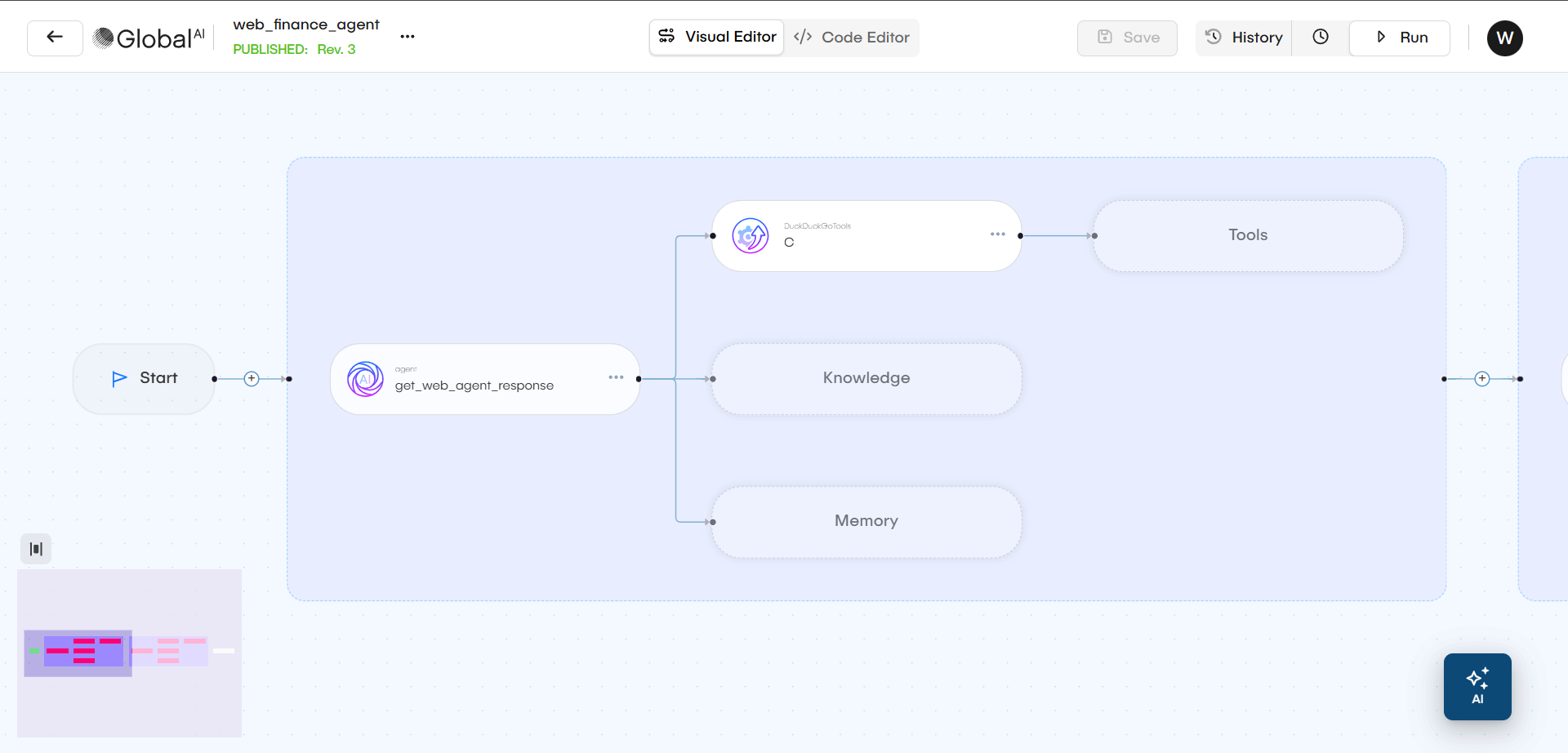
Understand AI Agent Components
When you configure an AI Agent, you are defining its "brain," "instructions," "hands," and "memory." This combination allows the agent to perform specific and useful tasks.
LLM Model and System Prompt
This is the agent's core "brain" and its "personality."
- LLM Model: You select a large language model (LLM) that will power the agent's reasoning. This can be a model from a provider like OpenAI or Gemini, or it can be a locally-hosted, open-source model running securely in your own environment.
- System Prompt: This is the set of instructions that defines the agent's purpose and rules. For example: "You are an IT support assistant. Your goal is to identify the user's problem and find the right contact in the IT department."
Tools
Tools are the agent's "hands." They give the agent functions it can perform to interact with other systems. An agent can use its reasoning to decide which tool to use based on your prompt.
- Predefined Tools: You can give an agent access to pre-built tools for common platforms, such as Jira.
- Custom Tools: You can create your own tools using Python. This allows your agent to connect to any internal API, proprietary database, or internal system. This is how you empower an agent to securely fetch data or perform actions within your own infrastructure.
Knowledge Base
This is the agent's "library." It provides the specific, private information the agent can access to answer questions. This ensures the agent's responses are based on your data, not just public information.
- Existing Database: You can connect the agent to an existing vector database (like Qdrant or Pinecone). This gives it a permanent library of your company's indexed knowledge.
- Runtime Files: You can have the agent scan files (like PDFs, DOCX, or CSVs) or websites at the start of a workflow. This creates a temporary knowledge base for that single task.
Memory
This is the agent's "notebook." Memory allows the agent to remember the context of a conversation.
Without memory, every message you send to the agent is a brand-new conversation. With memory, the agent can understand follow-up questions and refer to previous messages. This is essential for building chatbots or performing multi-step tasks. You can even configure memory to be shared between multiple agent nodes in a workflow.
Use Agents in Workflows
You can add an AI Agent as a node in a workflow, just like any other automation step.
- You configure the agent node with a prompt. This prompt can be dynamic by using variables from earlier steps in your workflow (for example: "Summarize the attached customer support ticket").
- The agent processes this prompt using its assigned model, tools, and knowledge.
- The agent produces a response (like a summary, a decision, or a piece of data it retrieved).
- The workflow receives this response as an output variable, which you can then use in the following steps.
Deployed Agents vs. Workflow Agents
You can use agents in two different ways, depending on your need for speed and persistence.
- Workflow Agent: This is an agent you configure "from scratch" inside a workflow node. The platform builds and runs this agent just for that specific workflow execution. This is useful for highly specific, one-time tasks.
- Deployable Agent: You can pre-build and deploy an agent configuration to make it "always-on." This deployed agent is much faster to respond because it is already running. You typically use deployed agents to power chatbots or to create a fast, reusable API endpoint for your AI.
Related articles
Now that you understand what an AI Agent is, you can learn how to build one and use it in your automations and how workflows work.
Use an AI Agent in a Workflow
A step-by-step guide to configuring and adding an AI Agent node to your automation workflow.
Workflows
This is the visual canvas where you design and execute your automation. A Workflow has several statuses, such as `draft`, `published`, and `active` (which counts towards your license).
Understand Actions
Learn about Actions in GlobalAI. This guide explains what Actions are, how they are used as reusable templates, and lists the available types.